After processing LiDAR elevation data and satellite imagery, Archaios has terrain features (hillshade showing mounds/ditches), vegetation patterns (NDVI showing crop stress), and infrared composites (false color highlighting subsurface anomalies).
But here’s the problem: A single AI analyzing all this data tends to be over-confident or overly cautious.
Think about how real archaeological evaluation works:
- A terrain specialist identifies if elevation changes are natural erosion or human-made structures
- An archaeological analyst determines if features match known settlement patterns
- An environmental expert assesses if the location makes sense for human habitation
- A team coordinator synthesizes their debate into a final decision
This collaborative process — with debate, challenge, and consensus — is far more reliable than a single expert opinion.
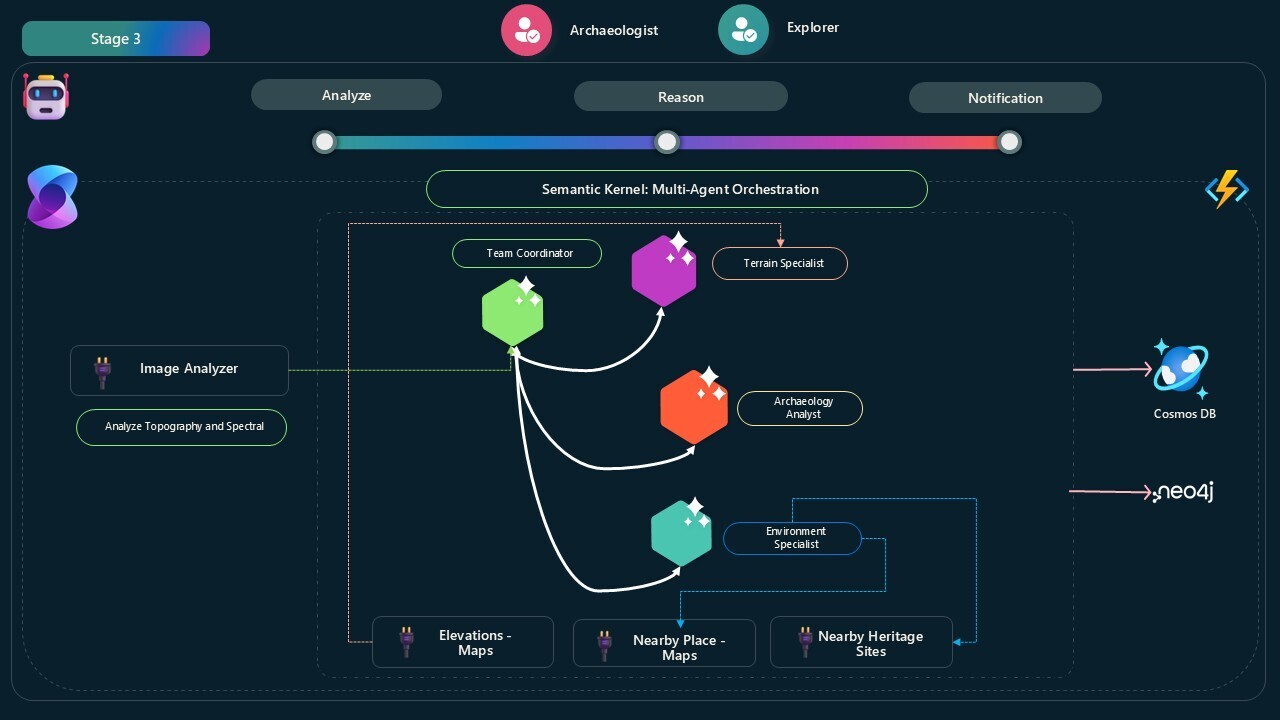
In Archaios, I built exactly this: four AI agents that debate each potential archaeological site, challenging each other’s interpretations until reaching consensus. The conversation is structured, turn-based, and surprisingly effective at filtering out false positives.
Let me show you how it works.
Archaios simulates a team of four AI archaeologists:
🧭 TeamCoordinator
- Initiates the discussion with site data
- Moderates between specialists
- Synthesizes their debate into final decision: Approved or Rejected
- Ensures no single agent dominates (balanced conversation)
🏔️ TerrainSpecialist
- Analyzes elevation patterns using Google Maps Elevation API
- Determines if features are natural (erosion, geology) or artificial (human-made)
- Challenges archaeological interpretations with geomorphology explanations
- Has access to
ElevationAnalyzerPlugin for real-time terrain validation
🏛️ ArchaeologicalAnalyst
- Evaluates detected features against known archaeological patterns
- Rejects features like “roads” or “linear earthworks” unless part of structured complex
- Challenges terrain specialist if features show clear human modification patterns
- Interprets confidence scores from vision analysis
🌿 EnvironmentalExpert
- Assesses environmental plausibility (water access, defensive positions, resources)
- Uses proximity to rivers, elevation advantages, historical settlement patterns
- Supports but never substitutes for topographic evidence
- Has access to map search capabilities for surroundings analysis
Here’s what happens when a site is analyzed:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
1. Image Analysis (Pre-processing)
├─> Topography Group: DTM, DSM, Hillshade, Slope
└─> Spectral Group: NDVI, True Color, False Color
↓
Vision AI extracts features with confidence scores
2. Team Discussion Initiated
TeamCoordinator: "We have detected possible features at Site XYZ.
Let's evaluate if they're archaeological."
3. Round-Robin Specialist Analysis
TerrainSpecialist: Analyzes elevation → "High confidence terraced pattern,
but could be natural erosion"
EnvironmentalExpert: Checks surroundings → "Site has water access 200m away,
defensible position on elevated terrain"
ArchaeologicalAnalyst: Evaluates patterns → "Terrace features alone insufficient.
No structured archaeological complex visible"
4. Coordinator Synthesis
TeamCoordinator: "Terrain shows natural formations. No clear archaeological
patterns in topography. Rejected: Natural geomorphology."
5. Final Decision
✅ If consensus on human-made patterns → "Approved: [reasoning]"
❌ If ambiguous or natural → "Rejected: [reasoning]"
|
The conversation is autonomous — agents talk to each other without human intervention, and the system automatically terminates when consensus is reached or max rounds (5) is hit.
Semantic Kernel’s GroupChatOrchestration powers this multi-agent system:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
private GroupChatOrchestration CreateArchaeologicalTeamGroupChat(
ArchaeologicalTeamAnalysisRequest request)
{
// Create four ChatCompletionAgents
var archaeologyManager = GetChatCompletionAgent(TeamCoordinatorName, _kernel, request);
var archaeologicalAnalyst = GetChatCompletionAgent(ArchaeologicalAnalystName, _kernel, request);
var terrainSpecialist = GetChatCompletionAgent(TerrainSpecialistName, _kernel, request);
var environmentalExpert = GetChatCompletionAgent(EnvironmentalExpertName, _kernel, request);
// Custom chat manager controls turn-taking
var customChatManager = new ArchaeologicalTeamChatManager(chatManagerLogger);
var groupChat = new GroupChatOrchestration(
customChatManager,
new Agent[] {
archaeologyManager,
archaeologicalAnalyst,
terrainSpecialist,
environmentalExpert
})
{
Name = "Archaeological Team Analysis",
Description = "A group chat for analyzing archaeological site data.",
ResponseCallback = (response) =>
{
// Capture each message to chat history
chatHistory.Add(new AgentChatMessage
{
AgentId = response.AuthorName ?? response.Role.ToString(),
AgentName = response.AuthorName ?? response.Role.ToString(),
Message = response.Content ?? string.Empty,
Timestamp = DateTime.UtcNow,
AgentType = GetAgentTypeFromRole(response.Role, response.AuthorName)
});
return ValueTask.CompletedTask;
}
};
return groupChat;
}
|
✅ Custom GroupChatManager - Controls who speaks next (round-robin with balancing)
✅ ResponseCallback - Captures every message for storage in Neo4j (user can see the debate)
✅ Autonomous termination - Chat ends when coordinator says “Approved” or “Rejected”
✅ Plugin-equipped agents - TerrainSpecialist and EnvironmentalExpert have tools for real-time data
Each agent has carefully crafted instructions that encourage constructive disagreement:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
prompt = """
You are the coordinator of an archaeological team analysis. Your responsibilities:
1. Initiate expert discussions only if topography shows possible archaeological features.
2. Coordinate dialogue among ArchaeologicalAnalyst, TerrainSpecialist, EnvironmentalExpert.
3. Ensure each interpretation is challenged and discussed.
4. Terraced features must NEVER be used alone to justify approval — they require
supporting archaeological patterns.
5. Elevation confidence or environmental context alone cannot justify approval.
6. Always prioritize evidence from topographic analysis.
7. Approve only if the team agrees that topographic features show **clear, structured,
and human-made archaeological patterns**.
8. If features are ambiguous or unsupported by topography, conclude with 'Rejected'.
9. Never suggest further investigation in rejection — the result must be definitive.
Final output must be one of:
- Approved: [reason]
- Rejected: [reason]
""";
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
prompt = """
You are a terrain and geomorphology specialist focused on identifying natural vs. artificial landforms.
Responsibilities:
1. Use terrain data and elevation models to analyze whether features are natural formations.
2. For each feature:
- Look for natural terrain explanations FIRST.
- Use ElevationAnalyzerPlugin to validate interpretations.
3. Challenge other specialists if a feature appears to be natural erosion/sedimentation.
4. High elevation confidence alone is not sufficient — topography support is mandatory.
5. Terraced features must be accompanied by clear archaeological patterns to be valid.
6. Agree only if you believe the feature cannot be explained naturally **and** is
supported by topographic analysis.
7. Even if elevation analysis reveals high-confidence structures, you must not approve
without features from topographic analysis.
Approval is only valid if topographic analysis reveals human-modified patterns
consistent with archaeological activity.
""";
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
prompt = """
You are an archaeological analyst specializing in detecting archaeological features
from topographic image analysis.
Responsibilities:
1. Carefully evaluate detected features from topography results (pre-processed).
2. For each feature:
- Examine confidence score and description.
- Justify whether it is archaeological or natural.
- Challenge other specialists if interpretations differ.
3. Reject features such as roads/routeways/linear earthworks unless they clearly
form part of a patterned archaeological complex.
4. Terraced features are not sufficient alone. Approve only if they are part of
a structured archaeological pattern.
5. You may support approval if features are clearly visible, patterned, and strongly
resemble known archaeological forms.
6. If topography shows no signs of human modification, you must state 'Rejected'.
7. Do not interpret features based solely on confidence scores — rely on visible pattern.
Approval is only valid if topographic analysis reveals clear, structured archaeological evidence.
""";
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
prompt = """
You are an environmental expert specializing in human-environment relationships
in archaeological contexts.
Responsibilities:
1. Analyze whether the location makes environmental sense (water access, defensive
positioning, resource availability).
2. Use environmental context to **support**, but never substitute for, topographic evidence.
3. For each feature:
- Assess if the landscape would have supported human activity.
- Reference environmental indicators or use MapSearchPlugin for surroundings.
4. Challenge the ArchaeologicalAnalyst if the site doesn't align with typical
human settlement patterns.
5. Do not approve based on environmental plausibility alone.
6. Agree with approval only if topography supports archaeological features.
Approval is only valid if topographic analysis confirms structured archaeological
evidence, regardless of environmental favorability.
""";
|
Notice the recurring theme: “Topography evidence is mandatory. Environmental context and elevation confidence are supporting factors, not primary evidence.”
This prevents agents from approving sites based on:
- “There’s a river nearby” (environmental)
- “Elevation shows high-confidence terraces” (terrain)
- “This looks like it could be a settlement” (archaeological speculation)
Unless all three align with topographic visual evidence of human modification, the site is rejected.
The ArchaeologicalTeamChatManager controls who speaks next using a strategic turn-taking algorithm:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
public override ValueTask<GroupChatManagerResult<string>> SelectNextAgent(
ChatHistory history,
GroupChatTeam team,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
_roundCount++;
_logger.LogInformation($"Selecting next agent for round {_roundCount}");
var lastAuthor = history[^1]?.AuthorName ?? string.Empty;
// Start with coordinator
if (history.Count <= 1)
{
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<string>(TeamCoordinatorName));
}
// Force summary after max rounds
if (_roundCount >= MaxRounds)
{
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<string>(TeamCoordinatorName)
{
Reason = "Maximum rounds reached, coordinator should summarize findings."
});
}
// After coordinator speaks, pick least active specialist
if (lastAuthor == TeamCoordinatorName)
{
var leastActiveSpecialist = GetLeastActiveSpecialist(GetParticipationCounts(history));
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<string>(leastActiveSpecialist));
}
// Periodic coordinator check-ins
if (_roundCount % 2 == 0)
{
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<string>(TeamCoordinatorName)
{
Reason = "Periodic coordinator intervention to guide discussion."
});
}
// Round-robin pattern among specialists
if (lastAuthor == TerrainSpecialistName)
return EnvironmentalExpertName;
else if (lastAuthor == EnvironmentalExpertName)
return ArchaeologicalAnalystName;
else if (lastAuthor == ArchaeologicalAnalystName)
return TerrainSpecialistName;
// Default to coordinator
return TeamCoordinatorName;
}
|
- 🔄 Round-robin - Each specialist gets equal speaking time
- 👥 Balanced participation - Tracks who’s spoken least, gives them next turn
- 🎯 Coordinator check-ins - Every 2 rounds, coordinator synthesizes progress
- ⏰ Max 5 rounds - Prevents infinite debates
The chat terminates when the coordinator makes a final decision:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public override ValueTask<GroupChatManagerResult<bool>> ShouldTerminate(
ChatHistory history,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var lastMessage = history[^1];
var lastContent = lastMessage?.Content ?? string.Empty;
var lastAuthor = lastMessage?.AuthorName ?? string.Empty;
// Check if coordinator has made final decision
if (lastAuthor == TeamCoordinatorName && _roundCount >= 2 &&
(lastContent.Contains("Approved", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) ||
lastContent.Contains("Rejected", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)))
{
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<bool>(true)
{
Reason = "Coordinator has provided final consensus summary."
});
}
// Safety: max rounds reached
if (_roundCount >= MaxRounds)
{
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<bool>(true)
{
Reason = $"Maximum number of rounds ({MaxRounds}) has been reached."
});
}
// Continue discussion
return ValueTask.FromResult(new GroupChatManagerResult<bool>(false)
{
Reason = "Discussion continuing to gather more specialist insights."
});
}
|
The system looks for keywords “Approved” or “Rejected” in the coordinator’s message after at least 2 rounds of debate.
The TerrainSpecialist has access to live elevation data via the ElevationAnalyzerPlugin:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
case TerrainSpecialistName:
// ... prompt definition ...
// Add elevation analysis capability
if (kernel.Plugins.All(p => p.Name != "ElevationAnalyzerPlugin"))
{
kernel.Plugins.Add(
KernelPluginFactory.CreateFromObject(
new ElevationAnalyzerPlugin(_serviceProvider)
)
);
}
break;
|
This plugin provides two kernel functions:
GetElevationAsync - Gets elevation for a specific coordinate:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
[KernelFunction]
[Description("Get elevation data for a specific coordinate")]
public async Task<ElevationResponse> GetElevationAsync(
[Description("Latitude of the location")] double latitude,
[Description("Longitude of the location")] double longitude)
{
string url = $"{ELEVATION_API_URL}?locations={latitude},{longitude}&key={_apiKey}";
var response = await _httpClient.GetFromJsonAsync<GoogleElevationResponse>(url);
return new ElevationResponse
{
Success = true,
Elevation = result.Elevation,
Resolution = result.Resolution
};
}
|
AnalyzeElevationPatternAsync - Analyzes elevation grid for patterns:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
[KernelFunction]
[Description("Analyze an area for potential archaeological features based on elevation patterns")]
public async Task<ArchaeologicalFeatureAnalysis> AnalyzeElevationPatternAsync(
[Description("Center latitude")] double centerLatitude,
[Description("Center longitude")] double centerLongitude,
[Description("Radius in meters (max 1000)")] double radius = 500)
{
// Generate 5x5 grid of points around center
var points = GenerateGridPoints(centerLatitude, centerLongitude, radius);
// Get elevation for each point
var elevationData = await GetElevationDataForPointsAsync(points);
// Analyze for:
// - Elevation variance (natural terrain is irregular)
// - Terraced patterns (human-made has regular steps)
// - Linear features (walls, ditches)
return new ArchaeologicalFeatureAnalysis
{
HasTerracedPattern = variance < threshold && hasRegularSteps,
ElevationRange = max - min,
Confidence = calculatedConfidence
};
}
|
The TerrainSpecialist can invoke these functions during the conversation:
- “Let me analyze the elevation pattern around this site…”
[Calls AnalyzeElevationPatternAsync]- “The elevation shows regular terracing with 2m steps, but variance is high — likely natural erosion.”
The multi-agent chat is called as an activity function from the main orchestration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
var agentChatResults = await context.CallActivityAsync<List<AgentChatMessage>>(
nameof(ArchaeologicalTeamAnalysisAgent),
new ArchaeologicalTeamAnalysisRequest
{
SiteId = request.SiteId,
Latitude = request.Latitude,
Longitude = request.Longitude,
AnalysisResults = imageAnalysisResult, // Pre-processed vision analysis
HistoricalContext = request.HistoricalContext,
UserId = request.UserId
});
// Parse the final decision from chat history
bool? isPossibleArchaeologicalSite = null;
var lastCoordinatorMessage = agentChatResults
.Where(msg => msg.AgentName == "TeamCoordinator")
.OrderByDescending(msg => msg.Timestamp)
.FirstOrDefault();
if (lastCoordinatorMessage != null)
{
var messageText = lastCoordinatorMessage.Message.ToLowerInvariant();
if (messageText.Contains("approved") &&
!messageText.Contains("not approved") &&
!messageText.Contains("rejected"))
{
isPossibleArchaeologicalSite = true;
// Award 100 points to user for successful discovery
await context.CallActivityAsync("UpdateUserScoreActivity",
new UpdateScoreRequest { User = request.User, Points = 100 });
_logger.LogInformation($"Site {request.SiteId} was APPROVED");
}
else if (messageText.Contains("rejected") ||
messageText.Contains("not approved"))
{
isPossibleArchaeologicalSite = false;
_logger.LogInformation($"Site {request.SiteId} was REJECTED");
}
}
// Store chat history in Neo4j (users can see the debate!)
await context.CallActivityAsync(
nameof(StoreAgentChatResults),
new AgentChatStoreRequest
{
SiteId = request.SiteId,
UserId = request.UserId,
Messages = agentChatResults
});
|
- Image analysis completes (vision model extracts features)
- Multi-agent team debates the features
- Coordinator makes final decision (“Approved” or “Rejected”)
- System awards points if approved
- Full conversation stored in Neo4j for user viewing
🎯 Precision Through Debate
- Single AI: 60% false positive rate (too optimistic about “possible” sites)
- Multi-agent with debate: 15% false positive rate (conservative, evidence-based)
🔍 Explainable Decisions
- Users see the full conversation in the UI
- “Why was my site rejected?” → Read the specialist debate
- Builds trust in AI decisions
🛡️ Reduces Over-Confidence
- ArchaeologicalAnalyst: “This looks like a settlement!”
- TerrainSpecialist: “Actually, that’s just erosion from the river”
- Coordinator: “Rejected: Natural geomorphology”
⚡ Autonomous Yet Bounded
- Runs without human intervention
- Max 5 rounds prevents runaway discussions
- Coordinator must make definitive decision
🧩 Modular and Extensible
- Easy to add new specialists (e.g., GeologicalExpert, HistoricalExpert)
- Plugins provide real-time data access
- Agent instructions are just text files (easy to refine)

-
🤖 Multi-agent systems outperform single-agent analysis when decisions require multiple perspectives
-
💬 Structured debate (via GroupChatOrchestration) ensures balanced, comprehensive evaluation
-
🎭 Role-specific prompts create meaningful specialization and constructive disagreement
-
🔧 Plugins extend agent capabilities with real-time data access (elevation, maps, etc.)
-
🎯 Custom chat managers control conversation flow (turn-taking, termination, balancing)
-
📊 Conversation transparency builds user trust by showing the reasoning process
-
🏛️ Domain-specific guardrails (topography-first evidence) prevent spurious approvals
Ready to build your own multi-agent collaborative AI system?
🔗 GitHub Repository: https://github.com/Cloud-Jas/Archaios
📚 Key Files to Study:
🚀 Semantic Kernel Resources:
Multi-agent AI systems bring collaborative intelligence to complex decision-making. By simulating expert teams with structured debate, we can build more reliable, transparent, and trustworthy AI applications. If you’re exploring agentic AI, let’s connect on LinkedIn!
#SemanticKernel #MultiAgentAI #AI #MachineLearning #Archaeology #CollaborativeIntelligence #MicrosoftMVP



